#Day6 of Mastering JavaScript Fundamentals: The Complete Guide to JavaScript30
Type Ahead
Type Ahead
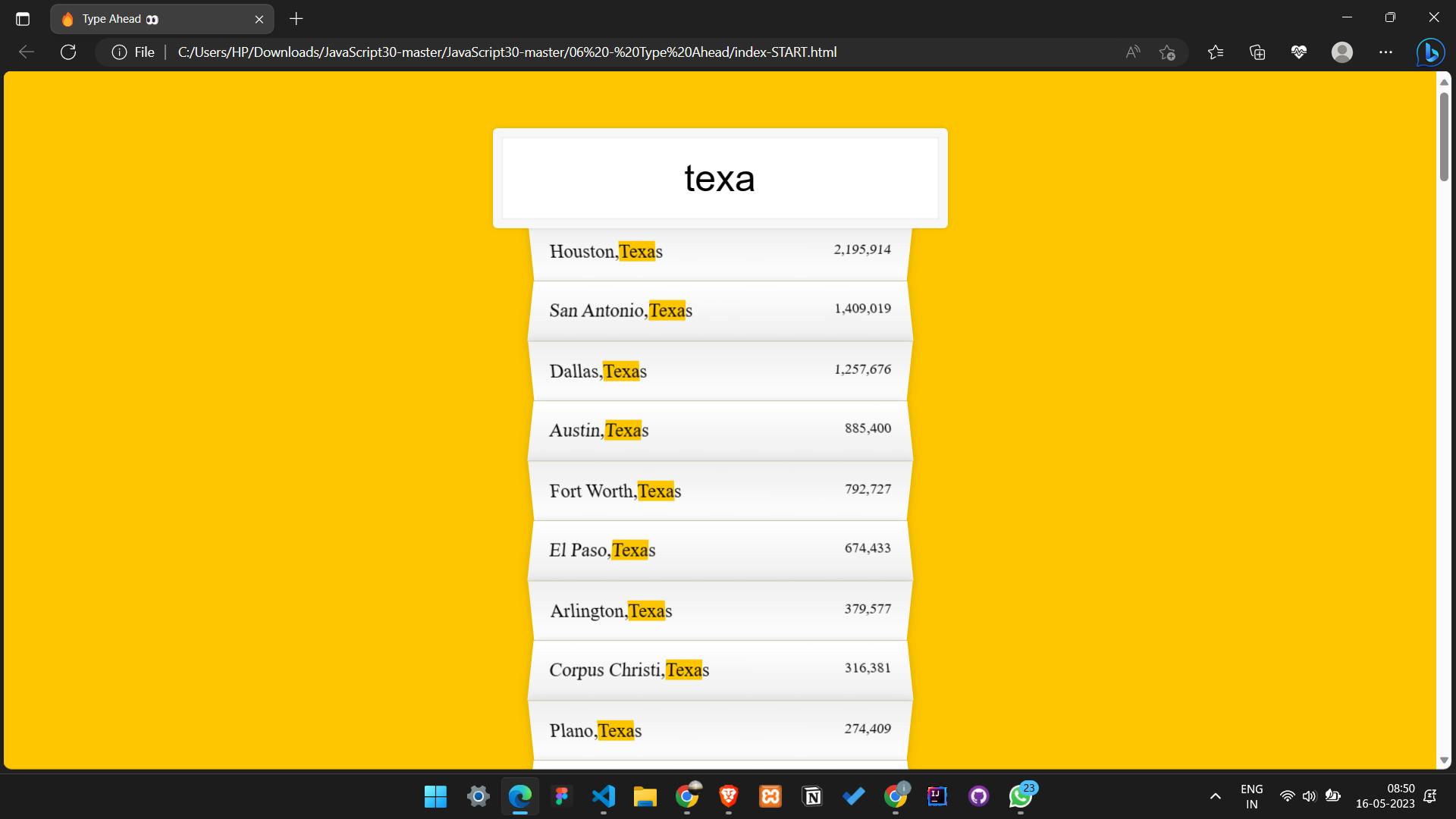
Type ahead, also known as autocomplete or predictive search, is a common feature in many modern web applications that allows users to search and find results quickly and efficiently. As the user types in their search query, the search bar suggests possible matches in real-time, giving the user a preview of the results they are likely to get. This feature can significantly improve the user experience of a website, as it saves time and effort by eliminating the need to type out the entire query. The Type Ahead project by Wes Bos is an excellent example of how to implement this feature using JavaScript and the DOM API.
Key Concepts Used in this Project
The key concepts used in the Type Ahead project include:
Fetch API:
The Fetch API is used to make HTTP requests to a server to retrieve data. In this project, it is used to fetch a list of cities and their corresponding state and population data.
Regular Expressions:
Regular expressions are used to match patterns in strings. In this project, regular expressions are used to filter the list of cities based on user input.
DOM manipulation:
The Document Object Model (DOM) is used to interact with HTML elements on a web page. In this project, the DOM is used to display the filtered list of cities and highlight the matching characters in the city and state names.
Event listeners:
Event listeners are used to listen for user input and trigger functions that update the display with the filtered results.
Template literals:
Template literals are a type of string literal that allows for embedded expressions. In this project, template literals are used to dynamically generate HTML for the filtered list of cities.
Guide for building the "type ahead" project
Step 1: Set up the HTML structure
Create an input element with a class of "search"
Create an unordered list element with a class of "suggestions"
<form class="search-form">
<input type="text" class="search" placeholder="City or State">
<ul class="suggestions">
</ul>
</form>
Step 2: Fetch the data
Fetch the data from the endpoint using the Fetch API
Parse the data into an array of objects
Store the array of objects in a variable
const endpoint = 'https://gist.githubusercontent.com/soyaine/8134b3a074068ab90111/raw/cities.json';
const cities = [];
fetch(endpoint)
.then(blob => blob.json())
.then(data => cities.push(...data));
Step 3: Create the search function
Create a function that takes in a search term and an array of objects
Filter the array of objects based on whether the city or state matches the search term
Return the filtered array
function findMatches(wordToMatch, cities) {
return cities.filter(place => {
const regex = new RegExp(wordToMatch, 'gi');
return place.city.match(regex) || place.state.match(regex);
});
}
Step 4: Create the display function
Create a function that takes in an array of objects and displays them in the DOM
Loop through the array of objects and create an HTML string for each object
Add the HTML string to the suggestions list in the DOM
function displayMatches() {
const matchArray = findMatches(this.value, cities);
const html = matchArray.map(place => {
const regex = new RegExp(this.value, 'gi');
const cityName = place.city.replace(regex, `<span class="hl">${this.value}</span>`);
const stateName = place.state.replace(regex, `<span class="hl">${this.value}</span>`);
return `
<li>
<span class="name">${cityName}, ${stateName}</span>
<span class="population">${place.population}</span>
</li>
`;
}).join('');
suggestions.innerHTML = html;
}
Step 5: Add event listeners
Add an event listener to the search input that calls the displayMatches function
Add an event listener to the search input for the "change" event that calls the displayMatches function
const searchInput = document.querySelector('.search');
const suggestions = document.querySelector('.suggestions');
searchInput.addEventListener('input', displayMatches);
searchInput.addEventListener('change', displayMatches);
That's it! You now have a working "type ahead" search bar that filters through a list of cities and states based on user input.
Summary
The Type Ahead project by Wes Bos is a JavaScript-based search tool that enables users to find matching cities and states from a pre-populated JSON dataset. As users type in the search box, the app dynamically filters the results and displays them in a dropdown menu. The project incorporates several key concepts, including the use of fetch API to retrieve data, the creation of a regular expression pattern to match search queries, and the implementation of a debouncing function to optimize performance. The end result is a simple yet powerful search tool that demonstrates the potential of JavaScript in building interactive web applications.
Other Reads
This blog provides a brief overview of the topics covered in the JavaScript30 course. For those looking for a quick review or to brush up on their JavaScript skills, this blog is a great resource. However, for a more comprehensive understanding of the topics covered, I highly recommend checking out the JavaScript30 course.
The JavaScript30 course covers a wide range of practical JavaScript projects that will help you build your skills and understanding of the language. The course is designed for anyone with a basic understanding of JavaScript and covers topics such as working with the DOM, manipulating CSS with JavaScript, making AJAX requests, and using ES6 features.
Overall, the JavaScript30 course is an excellent resource for anyone looking to improve their JavaScript skills and build practical projects. By following along with the course, you'll gain a solid understanding of the language and be able to apply your skills to real-world projects.
Reference
Other javascript30 Blogs to follow along